Mask and Parameters
General Parameters:
| V0 | Base value for PU conversion (kV) |
| F0 | Base value for PU conversion (Hz) |
Load Parameters:
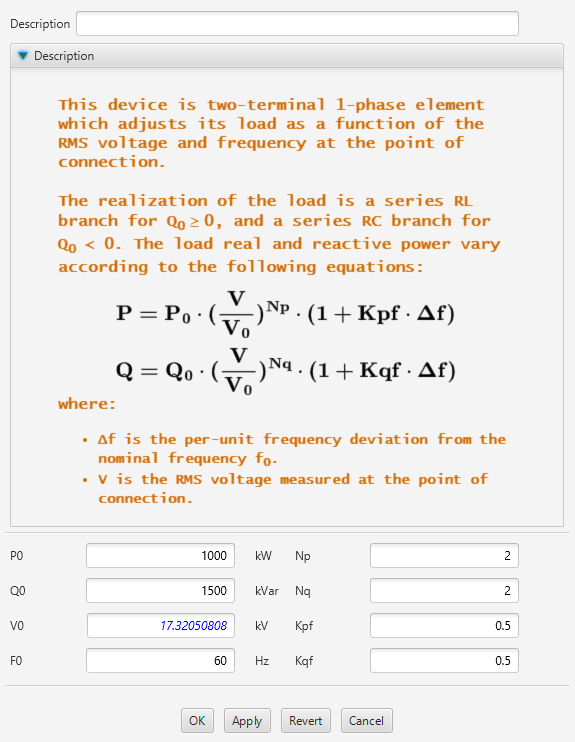
| Base active power (P0) | 1-phase active power under nominal conditions (kW) |
| Base reactive power (Q0) | 1-phase reactive power under nominal conditions (kW) |
| Np | Active power - Voltage variation coefficient |
| Nq | Reactive power - Voltage variation coefficient |
| Kpf | Active power - Frequency variation coefficient |
| Kqf | Reactive power - Frequency variation coefficient |
Ports, Inputs, Outputs and Signals Available for Monitoring
Ports
- Net_1: Network connection (supports only 1-phase connections)
- Net_3: Network connection (supports only 1-phase connections)
Inputs
- None
Outputs
- None
Sensors
- F: Estimated current at the point of connection
- Lout: Effective inductance or Capacitance
- Rout: Effective resistance
- Vrms: Estimated RMS voltage at the point of connection
Description of the Load Model
Load Model
The PQ load consists of the series combination of equivalent R, L and C branches and the series combination of equivalent R and L branches. The following rules are applied:
- If P=0 and Q=0, the element becomes disconnected in all solution methods.
- The RL series inductance equivalent is calculated using:
|
|
- The resistance value in the RL series combination is given by:
|
|
- When Q<0, the capacitance value becomes:
|
|
Model Equations
The model equations of this load are given by:
|
|
|
|
where:
: Active power under nominal conditions
: Reactive power under nominal conditions
: Nominal voltage
: Frequency deviation from the nominal value F0 in pu.
: Active power-Frequency coefficient
: Reactive power-Frequency coefficient
: Active power-Voltage coefficient
: Reactive power-Voltage coefficient
: RMS voltage measured between connection nodes Net_T1 and Net_T3
By adjusting Np and Nq equal to 0, 1, or 2, the load can be set to work as a constant power, constant current, or constant impedance, respectively.