The front panel of the OP7000V2 provides LEDs and connectors as described below.
A Primary FPGA board (OP7170-1)
This mandatory board is the main interface between the real-rime simulator and the OP7000V2 chassis.
From front top to bottom, the front plate of the board provides eight LED indicators in two rows.
The LED functions are as follows:
| Position | LED | Description |
|---|---|---|
Top row (left to right) | Power | Green indicates the unit is powered up |
Comm | Green indicates communication with the PC is active | |
Fault | Red indicates a fault | |
User-1 | Green/Yellow user-defined function | |
Bottom row (left to right) | Model | Green indicates the model is running on the real-time simulator |
Sync | Green indicates hardware synchronization is in Master mode Yellow indicates hardware synchronization is in Slave mode | |
Config | Green indicates the USER-defined bitstream is loaded in the FPGA Yellow indicates the SAFE (fallback) bitstream is loaded in the FPGA Flashing indicates the bitstream is not accessible, like during programming of the FPGA Off indicates there is no valid bitstream available in the internal flash memory of the card | |
| User-2 | Green/Yellow user-defined function |
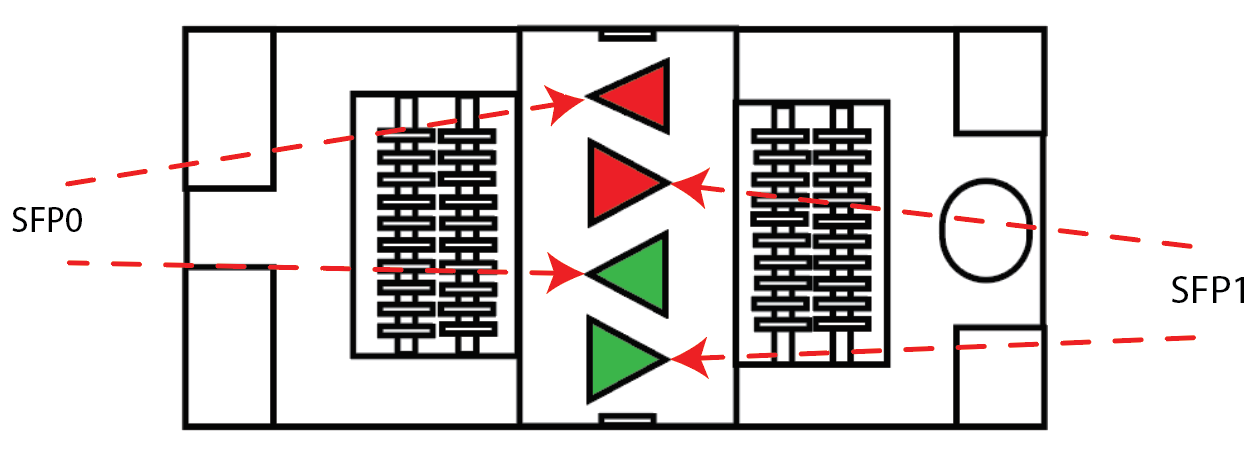
- Four SFP sockets, labeled SFP0 to SFP3, for high-speed communication with external devices. Controlled from the FPGA, these ports support either the MUlti-System Expansion link (MuSE) link for communication with other simulators' FPGAs, or generic Aurora communication with third-party devices.
Each socket controls one communication link. SFP transceivers and fiber optic cables must be selected according to the type and speed of the communication protocol implemented in the FPGA.
MUSE link requires specific SFP transceivers and optical fiber cable:
- SFP: Avago AFBR-57R5APZ
- Cable: LC-LC multimode 850nm optical fiber
Each socket has two LEDs. The LEDs are arrow-shaped to indicate the channels to which they are associated. The leftward arrows point to the left channel, the rightward arrows point to the right channel :
| LED | Color | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Green | ON = SFP is inserted OFF = no SFP present BLINK = channel active | |
| Red | OFF = no fault ON = transmission fault BLINK = reception loss |
- One 4-position dip-switch used to set the LSB of the Chassis ID
An additional 4-position dip-switch is located on the board's PCB as shown in the picture below :
By default, this internal dip-switch is set to 0, and the Chassis ID is then a value between 0 and 15.
Setting the internal dip-switch to a non-zero value allows the reading of Chassis ID values up to 255.
Note that this Chassis ID takes precedence over the rotary switches values of the OP7832 card.
- One mini-USB JTAG connector for FPGA programming.
This port is reserved for OPAL-RT technicians' or field application engineers’ use.
B Front interface slots
These sixteen slots, split into two groups of eight slots on each side of the Primary FPGA card, are used to install either I/O front interfaces (OP7220 or OP7353) or Secondary FPGA boards.
Note that the I/O interface placement in the above figure is only an example; the exact placement varies depending on the combination of I/O and FPGA cards required in the simulation.
C OP7220 analog I/O carrier or OP7353 digital font monitoring interface
Both of these interfaces provide:
- Sixteen green LEDs, organized in two columns of 8 LEDs labeled 0 to 7 and 8 to 15
- Each LED indicates activity on one of the sixteen I/O channels of the host
- Light intensity is directly commensurate to voltage (the higher the voltage, the brighter the LED intensity)
- One Status LED which indicates the following status or fault conditions
| LED | Description |
|---|---|
| Red | Insufficient power voltage for digital board |
| Blinking orange | Mezzanine ID does not match (applies to OP7220 only) |
| Orange | Sanity signal absent |
| Blinking green | Card is installed in an even-numbered slot instead of an odd one (applies to OP7220 only) |
| Green | Normal status, no fault |
- One column of 4 RJ45 connectors labeled CH 00-03, 04-07, 08-11, 12-15, to be used with the Monitoring connectors section, in order to visualize individual channels' activity on a monitoring device.
The placement of these interfaces must follow the compatibility constraints listed in the page OP7000V2 Adding or Replacing Boards
For more information on these boards, please refer to the OP7220 and OP7353 description pages.
D Secondary FPGA board (OP7170-2)
This board is under development, the description below is preliminary
When installed in one of the odd-numbered slots of the chassis, these optional boards provide the same front panel interface as the OP7170-1 Primary FPGA, however, some of the LEDs and connectors are not active on the OP7170-2 board.
Eight LED indicators in two rows. The LED functions are as follows:
Position LED
Description
Top row
(left to right)
Power
Green indicates the unit is powered up
Comm
Green indicates communication with the PC is active
Fault
Red indicates a fault
User-1
Green/Yellow user-defined function
Bottom row
(left to right)
Model
Green indicates the model is running on the real-time simulator
Sync
Green indicates hardware synchronization is in Master mode
Yellow indicates hardware synchronization is in Slave mode
Config
Green indicates the USER-defined bitstream is loaded in the FPGA
Yellow indicates the SAFE (fallback) bitstream is loaded in the FPGA
Flashing indicates the bitstream is not accessible, like during programming of the FPGA
Off indicates there is no valid bitstream available in the internal flash memory of the card
User-2 Green/Yellow user-defined function
- Four SFP sockets, labeled SFP0 to SFP3, for high-speed communication with external devices.
These ports support either Generic Aurora or OPAL-RT MuSE expansion links
- One 4-position dip-switch
These switches are not active on the OP7170-2.
- One mini-USB JTAG connector for FPGA programming.
This port is reserved for OPAL-RT technicians' or field application engineers’ use.
E Monitoring Connectors
This RJ45 to BNC panel is used to monitor I/O channels activity. Refer to section Connecting monitoring devices for connection instructions.
F Power switch with LED
This ON/OFF switch controls the power-up of the chassis. A Green LED indicates that power is ON.
Note that the back Power button must also be set to ON for the chassis to start.