Documentation Home Page ◇ HYPERSIM Home Page
Pour la documentation en FRANÇAIS, utilisez l'outil de traduction de votre navigateur Chrome, Edge ou Safari. Voir un exemple.
Advanced | SIMXSOM2
INTEGRAL MAXIMUM – [SIMXSOM2]
Computes the absolute maximum of an integral, a mean or a RMS value in a window moving over a signal resulting from a mathematical operation.
CATEGORY
Advanced
DESCRIPTION
The function allows to computes the absolute maximum of an integral, a mean or an RMS value in a window moving over a signal resulting from a mathematical operation between specific parts of two initial signals. A reject threshold can be applied to the first signal before the mathematical operation, in other words, the reject of the signal samples not reaching this threshold.
RESULT VARIABLES AND PARAMETERS
| Algebraic Maximum | Maximum of the input signal, multiplied by the factor. |
| Absolute Maximum | Absolute maximum of the input signal, multiplied by the factor. |
| Signal 1 | First input signal to perform analysis |
| Signal 2 | Second input signal to perform analysis |
| Threshold | Threshold to reach on the first signal to keep the sample. This threshold value must be positive since the absolute value of the sample is compared to it. The samples which do not exceed this threshold are considered as null. If this threshold is null, all the samples are automatically considered. |
| Signal_Part | Part of the signal on which the analysis is done (neg, pos, sig, abs). |
| Here are the definitions for the four distinct parts of a signal: | |
| Neg | Only the negative values of the input signal are used for the calculations. The other values are considered to be null. |
| Pos | Only the positive values of the input signal are used for the calculations. The other values are considered to be null. |
| Sig | The original input signal is used for the calculations. |
| Abs | The calculations are done on the absolute value of the input signal. |
| Operation_1 | Mathematical operation to execute between the two input signals (+,-,*,/). |
| Operation_2 | Operation to execute on the signal resulting from the mathematical operation in a window moving over it (int, moy, rms). The maximums of the integrals, means or rms values are kept.
|
| Window_Length | Time in seconds [s] during which the window moves over the analyzed signal. This time is reduced to the time of the analysis (ending time - starting time) if the window time specified is longer than the duration considered for the signal. This window time cannot be null. |
| Begin_time | Time at which the analysis of a signal must start. This time is expressed in milliseconds [ms]. This value must be greater than 0 and lower than the size of the acquisition buffer. The default value is 0. |
| End_time | Time at which the analysis of a signal must end. This time is expressed in milliseconds [ms]. The value of this time must be larger than the specified begin_time and smaller than the duration of the test. Use the “HUGE” value to specify the end of the test. The default value is HUGE. |
| Factor: | Multiplying factor for the results generated by the function. The default value of the multiplying factor is 1.0 and has no effect on the results. |
SYNTAX
[alg_max, abs_max] = simxsom1( input, "sig", 0, "int", 1/60, 0, HUGE, 1 )
CHARACTERISTICS
Data type support
Double Floating point
EXAMPLE
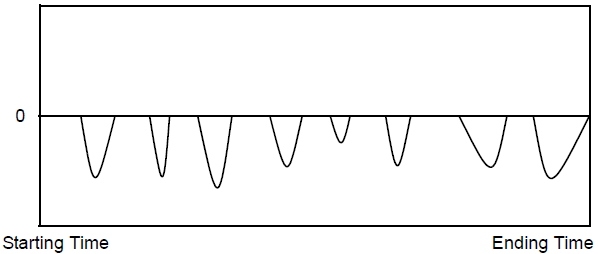
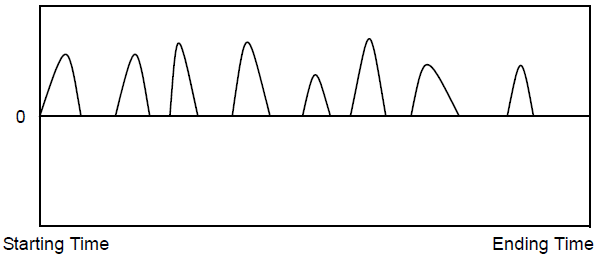
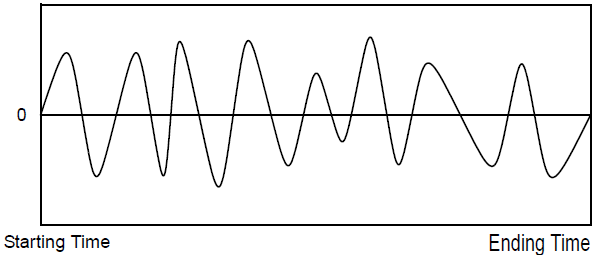
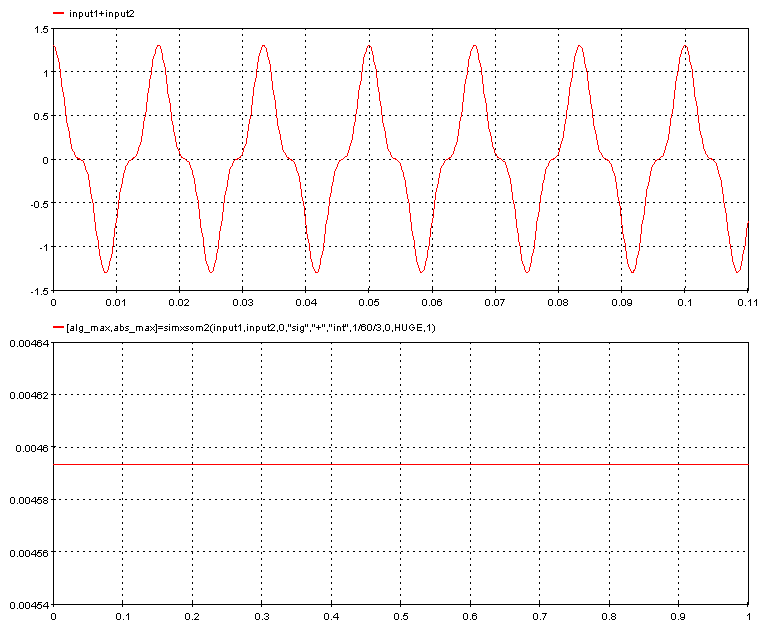
In the following example, the function compute the absolute maximum of the integral of the sum of two sine waves.
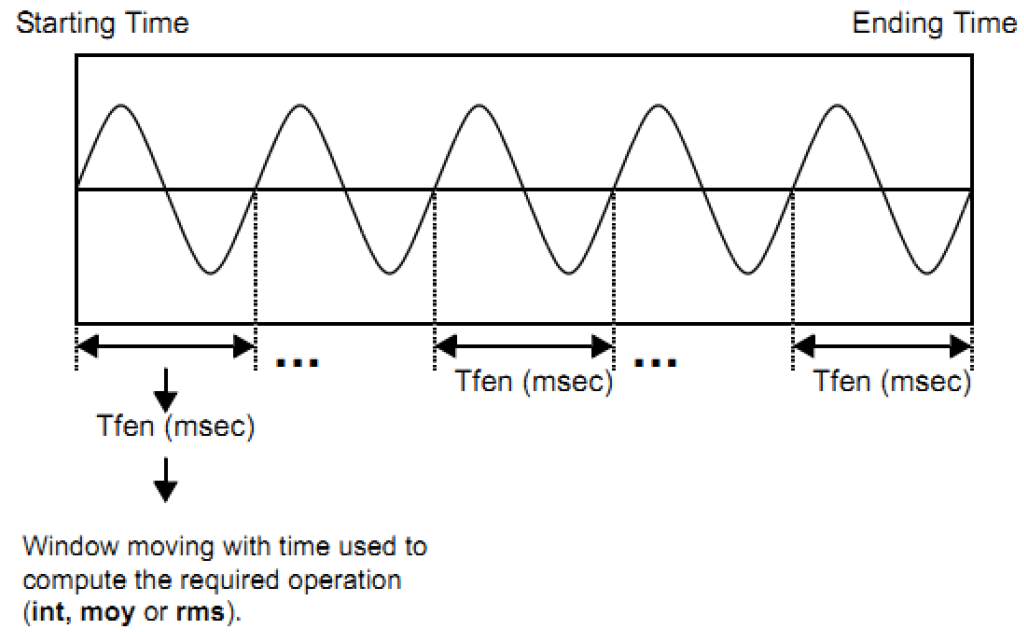
The following diagram shows the window moving over a signal based on the time specified for the window.
The operation is computed for each window from the start to the end of the limits and the function returns the maximum of the computed samples.
Let:
- nbech= number of samples to analyze for the signal
- lfen= number of samples in a window
- nbfen= number of windows for which the calculations are made
Then:
- nbfen=nbech-lfen+1
This set of points is used to find the maximum.
OPAL-RT TECHNOLOGIES, Inc. | 1751, rue Richardson, bureau 1060 | Montréal, Québec Canada H3K 1G6 | opal-rt.com | +1 514-935-2323
Follow OPAL-RT: LinkedIn | Facebook | YouTube | X/Twitter